Proxy a Kapa Hosted MCP server from your own MCP server
If you already expose an MCP server to your users, you can proxy Kapa’s Hosted MCP server to add Kapa’s semantic retrieval without requiring users to install multiple MCP servers.
The goal: your users connect to one MCP server (yours), but get access to both:
- Your native tools (execute commands, query product data, run workflows, update settings, etc.)
- Kapa’s ability to provide context from your knowledge sources.
This tutorial uses FastMCP as the concrete implementation, but you can apply the same proxy pattern in other MCP server frameworks too. The full example lives here: kapa-ai/fastmcp-proxy-example.
What is proxying?
In MCP, clients discover and invoke capabilities through standardized protocol methods like tools/list, tools/call, and resources/read.
Proxying means your MCP server acts as an intermediary:
- To the client, it looks like a normal MCP server.
- Behind the scenes, it forwards some (or all) MCP requests to another MCP server, then relays the response back to the client.
In this example, we forward requests to Kapa’s Hosted MCP server so Kapa’s semantic search shows up alongside your native tools.
┌───────────────────────────────────────--─┐
│ Your MCP Server │
│ │
│ • get_status (native) │
│ • search_your_product_knowledge_sources |──► Kapa Hosted MCP server
│ │
└───────────────────────────────────────--─┘
When should you proxy?
Proxying is a good fit when you want to:
- Keep one installation for end users (Cursor, Claude Desktop, etc.)
- Bundle your product tools + knowledge retrieval behind one endpoint
- Add custom behavior around Kapa tools (auth, logging, filtering, routing)
Prerequisites
To follow this guide, you’ll need:
- Docker
- A Kapa project with a Hosted MCP server configured
(and an API key you can use server-side)
If you don’t have a Hosted MCP server yet, follow Hosted MCP server setup, then come back here.
1. Clone and run the example
Create your .env file:
cp env.example .env
Edit .env with your Hosted MCP credentials from Kapa:
KAPA_MCP_SERVER_URL=https://your-project.mcp.kapa.ai
KAPA_API_KEY=your-kapa-api-key
Keep your
KAPA_API_KEYserver-side. Do not embed it in client apps.
Now run the example:
docker compose up
This starts two containers:
- MCP Server (
http://localhost:8787):- a small native tool (
get_status) - Kapa tools mounted via a proxy
- a small native tool (
- MCP Inspector (
http://localhost:6274) �— a web UI to browse and test MCP tools
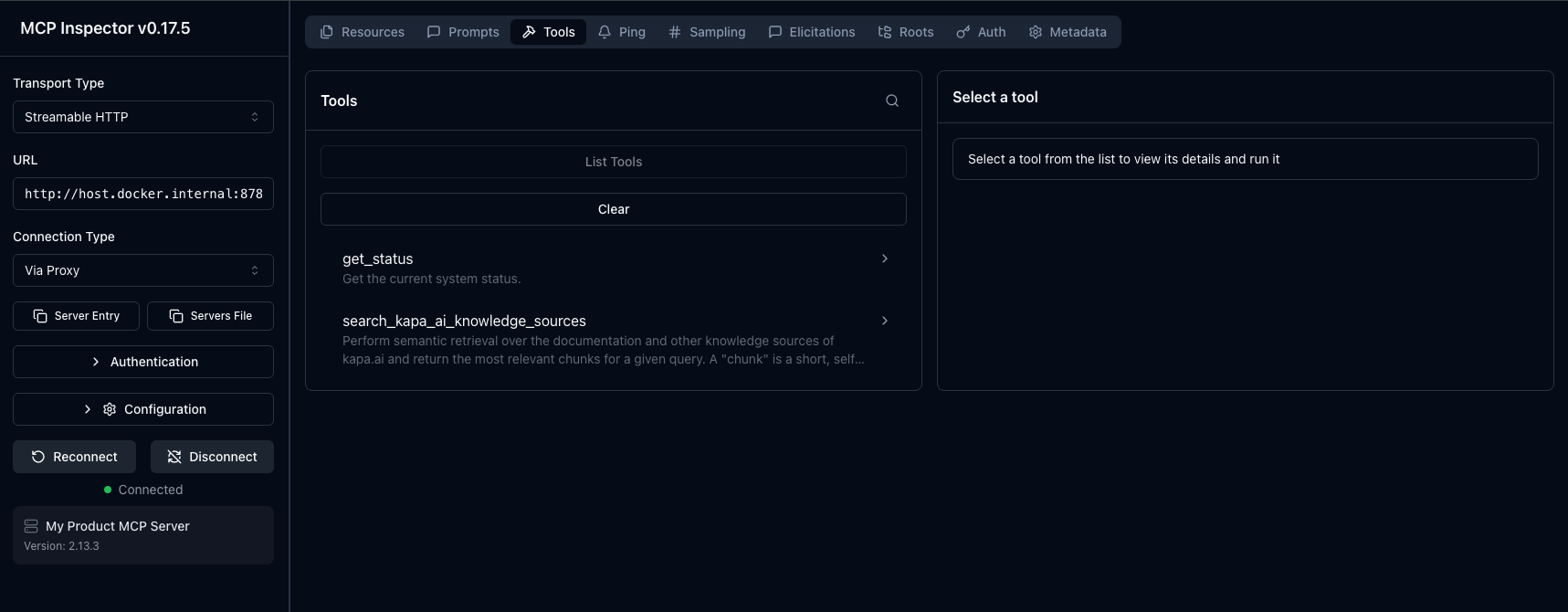
2. Verify in the MCP Inspector
Open the Inspector:
- Go to
http://localhost:6274 - The server URL should be prefilled — click Connect
- Go to the Tools tab
You should see:
get_status: your native toolsearch_your_product_knowledge_sources: proxied from Kapa
3. Try it: call both tools
In the Inspector’s Tools tab:
- Call
get_status→ you should get something like{"status": "healthy"} - Call
search_your_product_knowledge_sourceswith a query from your docs, e.g.:query: "webhooks rate limits"query: "SSO setup"query: "how to rotate API keys"
4. Understand how it works
At a high level, your server becomes the single MCP endpoint your users connect to.
Inside that server, you expose two kinds of capabilities:
- Native tools implemented by your server (execute commands, query product data, run workflows, etc.)
- A proxied connection to Kapa’s Hosted MCP server, so your server can forward certain MCP requests upstream and return the results to the client
In practice, this is just server composition: your server “mounts” a proxy server, and FastMCP presents everything as one combined MCP server to the client.
Here’s what that looks like in code:
import os
from fastmcp import FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP(name="My Product MCP Server")
# Your native tool
@mcp.tool
def get_status() -> dict:
return {"status": "healthy"}
# Create proxy to Kapa's Hosted MCP server
kapa_proxy = FastMCP.as_proxy({
"mcpServers": {
"kapa": {
"url": os.getenv("KAPA_MCP_SERVER_URL"),
"transport": "http",
"headers": {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {os.getenv('KAPA_API_KEY')}",
},
}
}
})
# Mount Kapa's tools into your server
mcp.mount(kapa_proxy)